Expansion Valves
What do Expansion Valves do?
An expansion valve is a metering device that speeds up or slows down the refrigerant flowing into the evaporator. Think of them as a tap; the hotter it is, the more refrigerant you need so the valve will open. The cooler it is, the less refrigerant you need, so the valve will close. The expansion valve slows the refrigerant down and allows just enough liquid through, so in the evaporator it changes from a liquid to a gas; absorbing more heat and leaving about 1/4 of the top of the evaporator completely gas (superheat). If liquid refrigerant gets through, there is nothing stopping it from getting to the compressor. Compressors do not compress liquid, and it will be destroyed.
An expansion valve is a metering device that speeds up or slows down the refrigerant flowing into the evaporator. Think of them as a tap; the hotter it is, the more refrigerant you need so the valve will open. The cooler it is, the less refrigerant you need, so the valve will close. The expansion valve slows the refrigerant down and allows just enough liquid through, so in the evaporator it changes from a liquid to a gas; absorbing more heat and leaving about 1/4 of the top of the evaporator completely gas (superheat). If liquid refrigerant gets through, there is nothing stopping it from getting to the compressor. Compressors do not compress liquid, and it will be destroyed.
What Types of Expansion Valves are there?
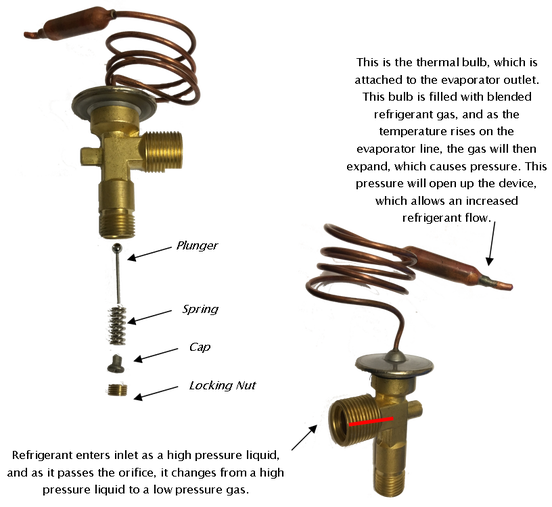
Internally Equalized-In an internally equalized expansion valve, refrigerant enters at the inlet, and has to pass through a metered device, which restricts the refrigerant. As the refrigerant routes through the device, it passes from the high side to the low side of the system.
Internally Equalized-In an internally equalized expansion valve, refrigerant enters at the inlet, and has to pass through a metered device, which restricts the refrigerant. As the refrigerant routes through the device, it passes from the high side to the low side of the system.
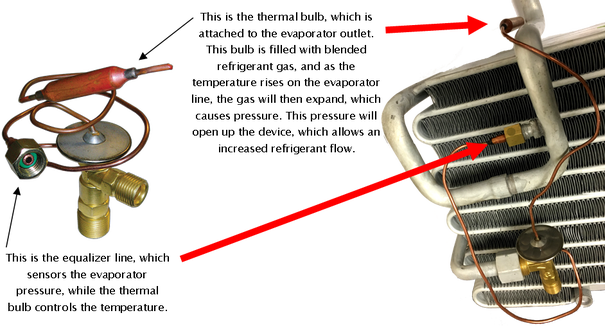
Externally Equalized-In an externally equalized expansion valve, the process of refrigerant flow is the same; however this expansion valve contains a line with a nut. This line, known as the equalizer line, is attached to the outlet of the evaporator.
Block Expansion Valve– Just as the externally and internally equalized expansion valves, the block valve provides the restriction needed to change the high pressure liquid to a low pressure gas. Refrigerant enters through the bottom opening with the quantity determined by the sensor bulb. This sensor bulb is filled with a small amount of refrigerant. This bulb monitors the temperature of the refrigerant vapor which is exiting the evaporator. As the temperature rises, the sensor heats up the liquid refrigerant, which is enclosed in the diaphragm. The refrigerant expands once heated, which then moves the plunger downwards. When the device is moved downwards, there is an increase of flow of refrigerant to the evaporator. Once the temperature falls, the device closes, and the refrigerant in the diaphragm begins to cool. Then, it raises the plunger to slow the flow of refrigerant.
| gpd_tech_tip_49-how_it_works-expansion_valves.pdf |